What is Difference Between Hydroponics, Aquaponics & Aquaculture?
In today’s agricultural climate, we’re continually searching for new and better ways to grow and provide the food that people need to be healthy without harming the environment. To this end, there are several trends currently shaping our food production system. You may have heard words like hydroponics, aquaculture, and aquaponics. What are these practices, and how are they different? Read on to find out.
What is Aquaculture?
In a traditional aquaculture system, fish are grown in contained environments, as aquatic livestock. Sometimes these are nets or other structures placed within natural water habitats. Other times these are tanks or human-made ponds, cut off from natural water sources. When growing fish in human-made facilities, growers must carefully filter the water to remove fish waste and maintain a healthy habitat.
Unfortunately, these fish farms are notoriously bad for the environment. Factory fish farms are the large aquaculture operations that provide us with about half of the fish we consume. They are widely considered to be one of the least sustainable types of agriculture. Because of the crowded conditions necessary for such an operation, the water becomes highly polluted. Wastewater from factory fish farms includes high levels of fish waste, but also antibiotics, pesticides, and hormones, and all of this winds up in our waterways and oceans.
What is Hydroponics?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil. Instead, plant roots have direct access to water sources that contain all of the nutrients they need to grow and thrive. These systems are often indoors, with controlled microclimates allowing for precise environmental conditions to ensure maximum plant growth with minimal exposure to risks like pests, frost, flooding, and the like. This will enable growers to harvest a significant quantity of high-quality produce with almost no chance of loss due to climate or contamination.
These vertical indoor farms can be grown in areas where there is no space for traditional agriculture. They can also grow year-round, regardless of climate or weather conditions. For many, it is a great hope that hydroponic farms will eliminate food deserts, providing fresh and healthy greens and other produce to underserved communities.
Hydroponics, when done correctly, is also an incredibly sustainable practice. Surprisingly, it uses far less water than traditional agriculture by recycling water through the system again and again. It also doesn’t contribute to soil degradation, a significant concern in the world today.
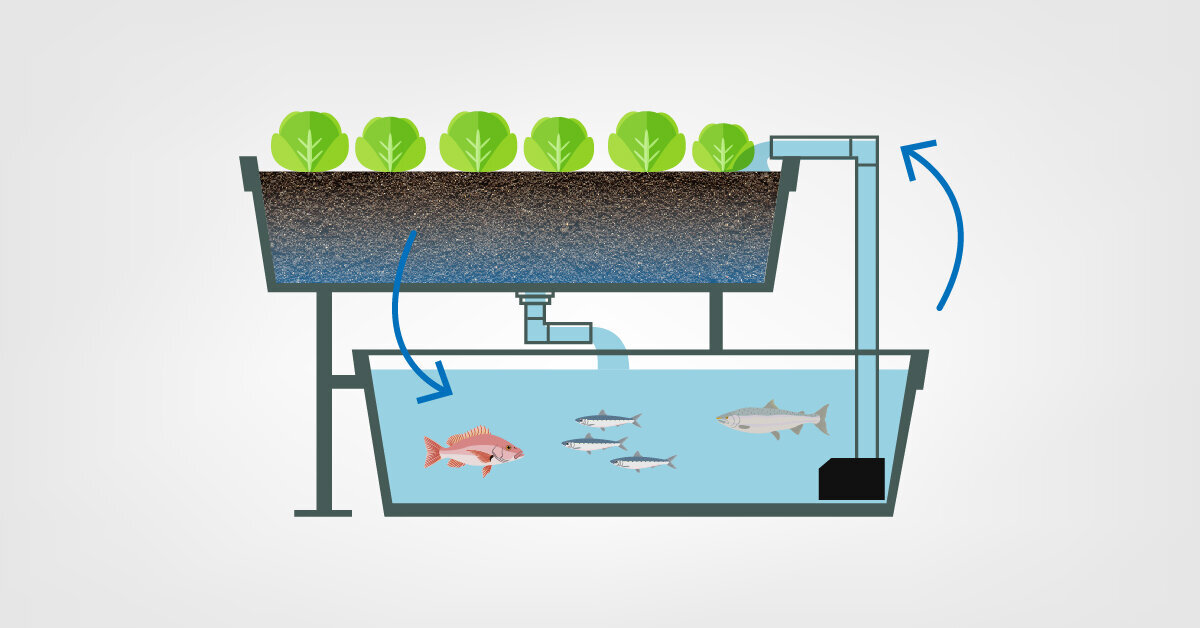
What is Aquaponics?
Source: Americover
Aquaponics, then, blends these two systems and balances them together. Plants filter the water by pulling fish waste out of it. The fish waste provides nutrients that the plants need to grow. In most cases, the growers supplement with additional nutrients to create ideal growing conditions for aquaponic crops. An aquaponics system functions as a symbiotic relationship in which the fish provide nutrients to the plants and the plants keep the fish healthy by cleaning their water.
Of course, this symbiotic system gives all of the environmental benefits of a traditional hydroponics system and eliminates factory fish farming’s worst environmental problems. It also largely removes the health problems associated with eating factory-farmed fish. For those looking to grow healthy fish on a commercial scale without destroying our precious waterways, aquaponics is an excellent choice.
If you’re looking for a sustainable way to grow fresh, healthy food on a commercial scale, consider a hydroponic greenhouse from Eden Green Technology. With our advanced systems, nutritious, fresh, and safe food is both sustainable and practical. Contact us today for more information.